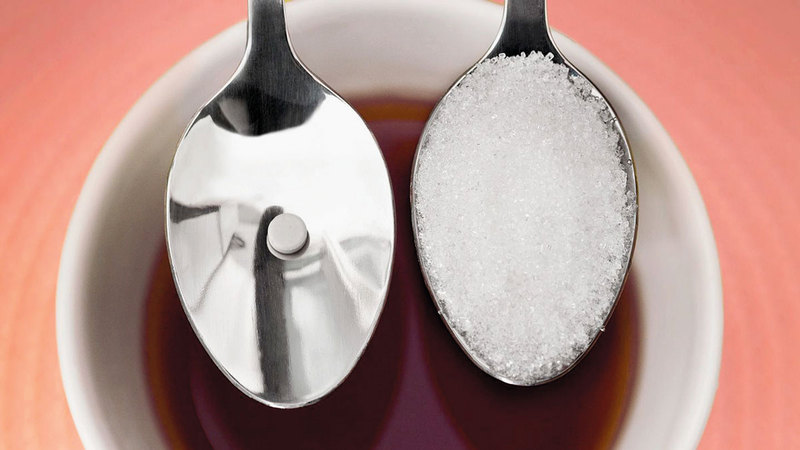
In light of recent research, xylitol, a common low-calorie sweetener found in sugar-free products such as gum, toothpaste, and various food items, is being scrutinized for its potential health risks. A study from the Cleveland Clinic indicates that high consumption of xylitol may be linked to a two-fold increased risk of heart attacks, strokes, and related deaths. Dr. Stanley Hazen, lead author and director of the Center for Cardiovascular Diagnosis and Prevention at the Cleveland Clinic, explains that xylitol levels in the blood can increase drastically when consumed in typical quantities, potentially leading to serious health issues.
The study suggests that xylitol, much like another sweetener called erythritol, may cause platelets to clot more easily, increasing the risk of life-threatening cardiovascular events. Concern arises as these blood clots can travel to critical areas such as the heart and brain, resulting in heart attacks and strokes. The research highlights that these sweeteners activate platelets significantly, even in small amounts typically consumed in everyday products.
Xylitol, which has been popularized for its lower calorie content compared to sugar, is present in various consumer goods, labeled as keto-friendly, diabetic-friendly, or low-sugar alternatives. However, recent findings raise questions about its safety, and experts recommend reevaluating its consumption. Dr. Matthew Toomey from Mount Sinai Foster Heart Hospital, although not part of the study, emphasizes that while the experiments are revealing, they do not conclusively prove that platelet abnormalities directly cause the observed clinical events.
Given the increasing prevalence of cardiovascular diseases, with projections indicating that around 61% of American adults may develop such conditions by 2050, Dr. Andrew Freeman from the National Jewish Health Center warns against the additional risk posed by these sweeteners. He advises prioritizing natural sugars like honey or fruit and limiting artificial sweeteners to prevent potential health risks. Despite this, xylitol remains widely used in various products, necessitating informed choices by consumers.
Furthermore, Dr. Sadiya Khan from Northwestern Medicine stresses the need for high-quality dietary components such as fruits and vegetables over artificial sweeteners. Khan asserts that while the study does not prove causality, it is prudent to moderate artificial sweetener intake until further research provides clearer conclusions.
For people at high risk of cardiovascular diseases or those already diagnosed, the insights from this study are particularly pertinent. Reducing the intake of sugar alcohols like xylitol, which have seen a rise in popularity parallel to increasing obesity rates, could contribute to overall cardiovascular health. With experts like Joanne Slavin, a nutrition professor at the University of Minnesota, echoing the call for moderation, it is evident that the debate over artificial sweeteners and their health implications will continue.
- Xylitol is a sugar alcohol that is naturally found in small amounts in fruits and vegetables. As an additive, it is used extensively in sugar-free gum, candies, toothpastes, and baked goods.
- The human body also produces xylitol, which has led to its widespread acceptance. However, the quantities used in consumer products are significantly higher than those naturally occurring.
- Medical professionals recommend drinking water, unsweetened tea, or coffee as alternatives to beverages and foods containing artificial sweeteners.
- Despite regulatory approvals for sweeteners like xylitol and erythritol, recent studies call for a reassessment of their safety based on emerging evidence.